08 March 2023: Human Study
Study of 60 Adult Patients to Compare Standard Postoperative Clinical Assessment with Train-of-Four Ratio ≥0.9 on Patient Outcomes Using Postoperative Spirometry and Neuromuscular Function Measurements Following Extubation
Chunlong Chen AEF , Qingzhen Liu CD , Hong Fan BD , Zhiyang Yu CF , Xueyan Leng B , Lidong Zhang ADF , Zhiqiang Zhou ADE*DOI: 10.12659/MSMBR.938849
Med Sci Monit Basic Res 2023; 29:e938849
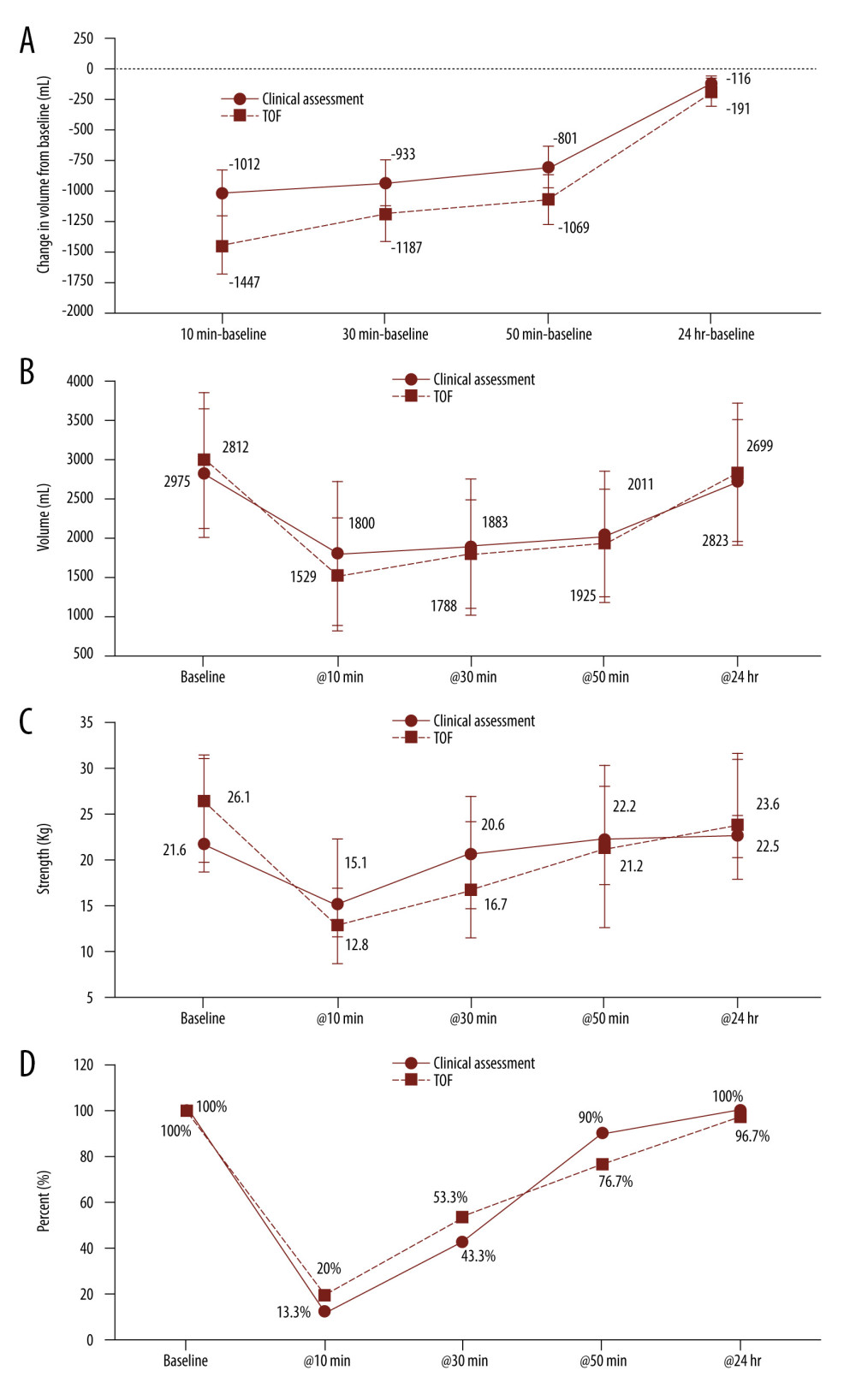
Figure 2 Strength measurements of different time points. (A) Change from baseline spirometry volume varies with time; (B) absolute incentive spirometry volume varies with time; (C) handgrip strength varies with time; (D) ability to sit up varies with time. (A) Data are shown with (median, IQR); IQR – interquartile range; * P<0.05 when compared with clinical assessment group at the same time point; (B) Data are shown with (Mean, Std), Std – standard deviation; there was no significant difference between the two groups at the same time point; (C) Data are shown with (Median, IQR), there was no significant difference between the two groups at the same time point; (D) Data are shown with (Proportion of Total), there was no significant difference between the 2 groups at the same time point. @10 min – time point of 10 min after extubation; @30 min – time point of 30 min after extubation; @50 min – time point of 50 min after extubation; @24 h – time point of 24 h after extubation.


